Loose File in Cyber Forensics: A Vital Forensic Insight
A loose file in cyber forensics refers to files without their original metadata or directory path. It is typically found in unallocated space and can be recovered using file carving methods.
In digital forensics, not everything is neatly organized in folders with names and timestamps for digital evidence analysis. Most of the time, examiners encounter something a bit messier: Loose Files. These are fragments of data that have been deleted, hidden, or left behind during system failures or cyber incidents.
They are not visible through normal file system navigation because they have lost their meta details or directory structure. However, do not make any mistake, as loose files can hold critical evidence in cyber forensics.
What are the Causes of Loose Files?
Now let’s explore how files become loose in the first place. Knowing the causes of loose files is crucial in any cyber forensic investigation, as it offers context to your findings and helps explain user intent, system behavior, or malicious activity. Mentioned below are some of the common scenarios where loose files are generated:
1. File Deletion
The most common cause of loose files is straightforward deletion. When a user deletes a file, the system removes its metadata but not necessarily the file content. It remains in unallocated space. Sometimes fully intact until it’s overwritten. This is a prime hunting ground for forensic investigators.
2. System Crashes or Power Failures
Unexpected shutdowns can disrupt file-writing operations that leave behind orphaned data. These fragments may not be associated with any proper file path or record, but they still exist on the disk and can be vital in reconstructing lost or corrupted evidence.
3. Malware Activity
Sophisticated malware often creates or deletes files without generating corresponding system logs. For example, create temp files and delete them immediately after execution. These loose files can detect malware presence and behavior.
4. Formatting and Reinstallation
Even after formatting a drive, some files survive, especially on quick formats. This is particularly true for file systems like NTFS, where data isn’t fully wiped unless a secure erase method is used.
Understanding these scenarios helps you prioritize search areas and predict where evidence may reside. This empowers you to uncover loose file artifacts that others might overlook.
Best Method to Identify Loose File in Cyber Forensics
The best way to analyze the loose files in cyber forensics is to opt for advanced email forensic software named MailXaminer. This software is not just a solution, but it’s a comprehensive investigative platform. When it comes to investigating the loose files, it provides you an multiple options to add evidence as EML, EMLX, MSG, and PDF as a zip file. This advanced software provides you offers a well-integrated suite of capabilities to assist digital forensic experts.
Let’s see how software helps cyber forensic experts to analyze loose files
Step 1. Set up the software on your system, and add a case.
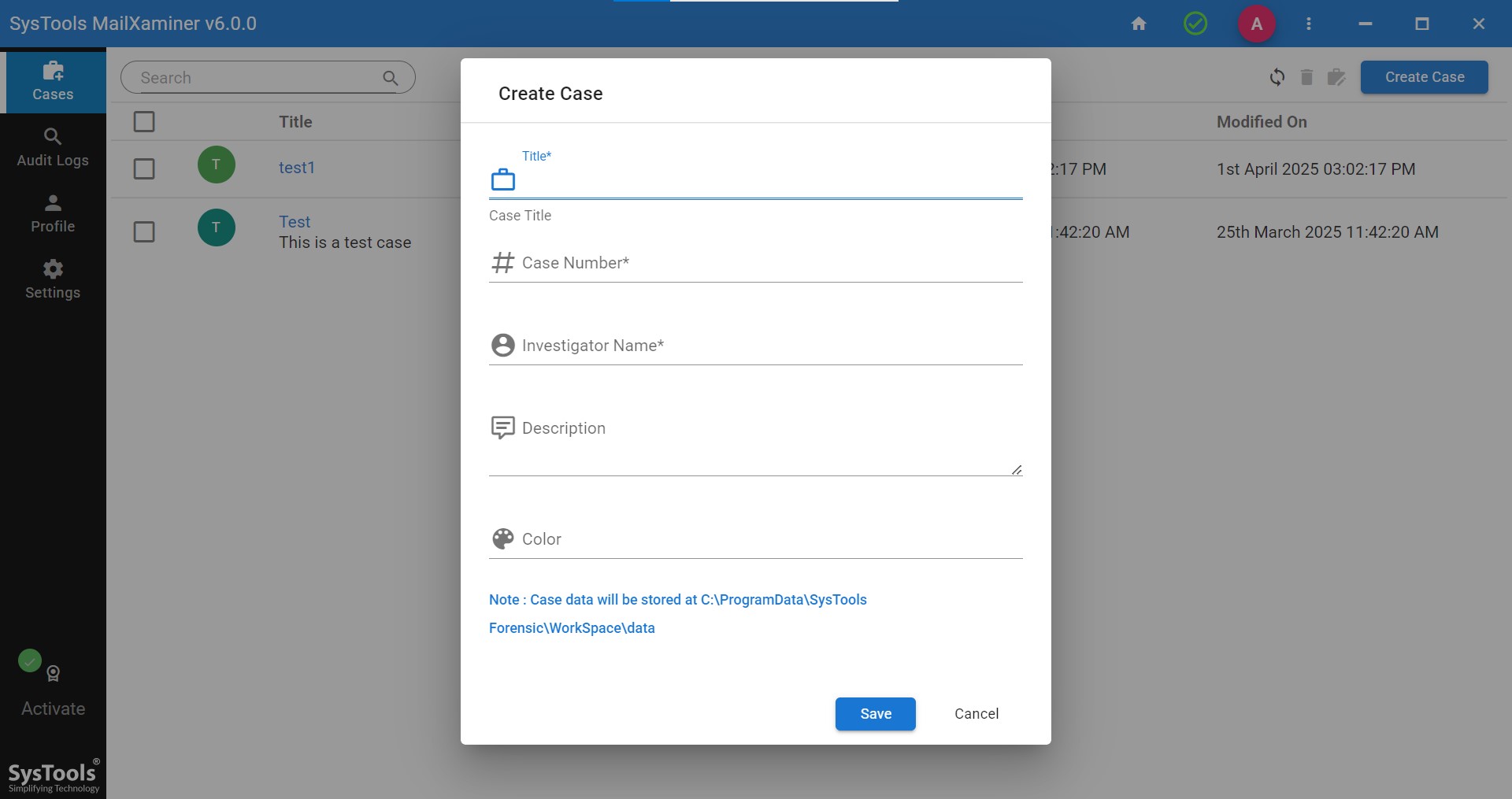
Step 2. After adding the case, add the evidence as an image.
Note- Here we zip the PDF files, you can zip your files as per your preference, file format

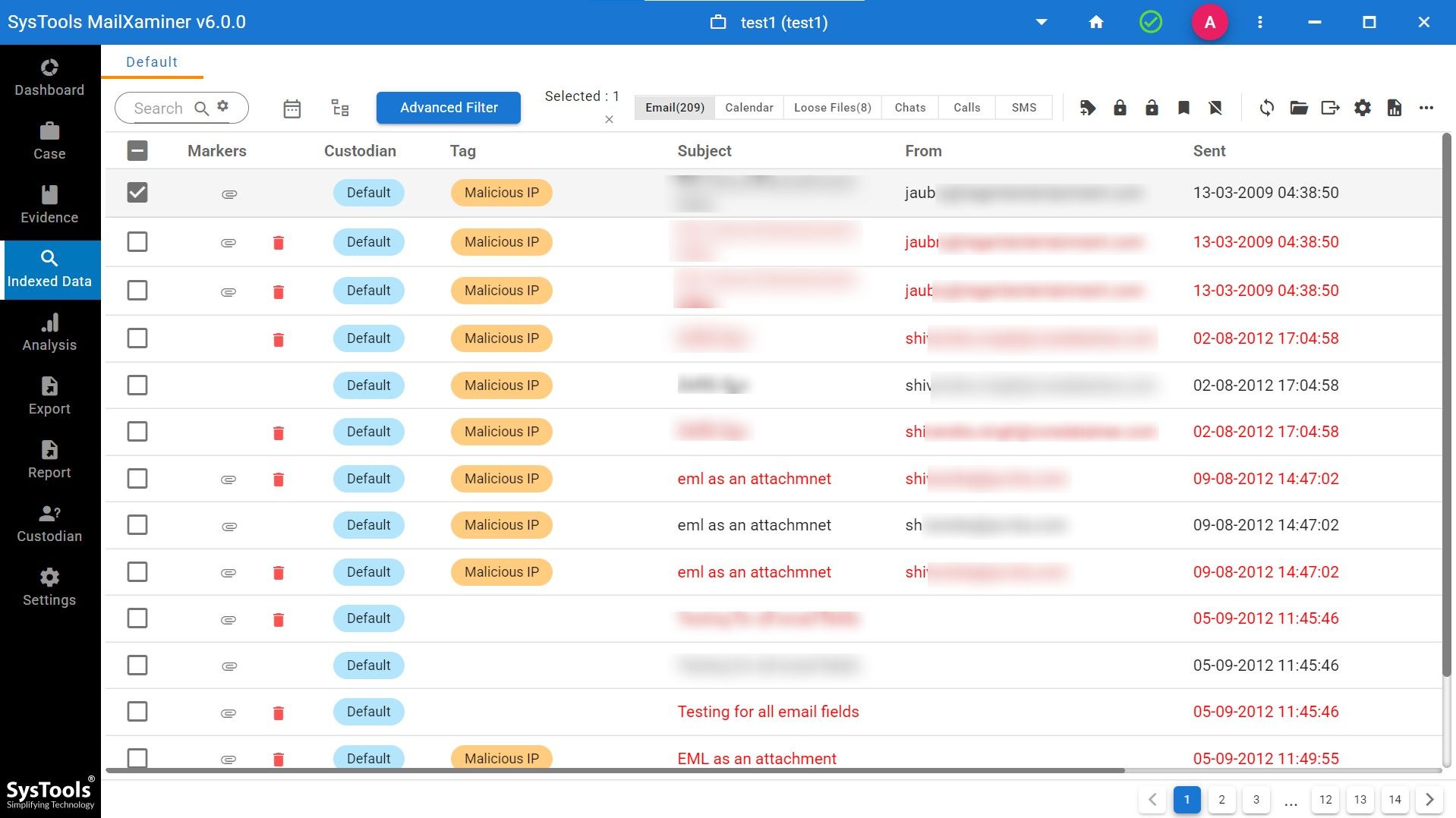
Step 3. Then complete indexed data is visible in the software dashboard as seen in the screenshot below.
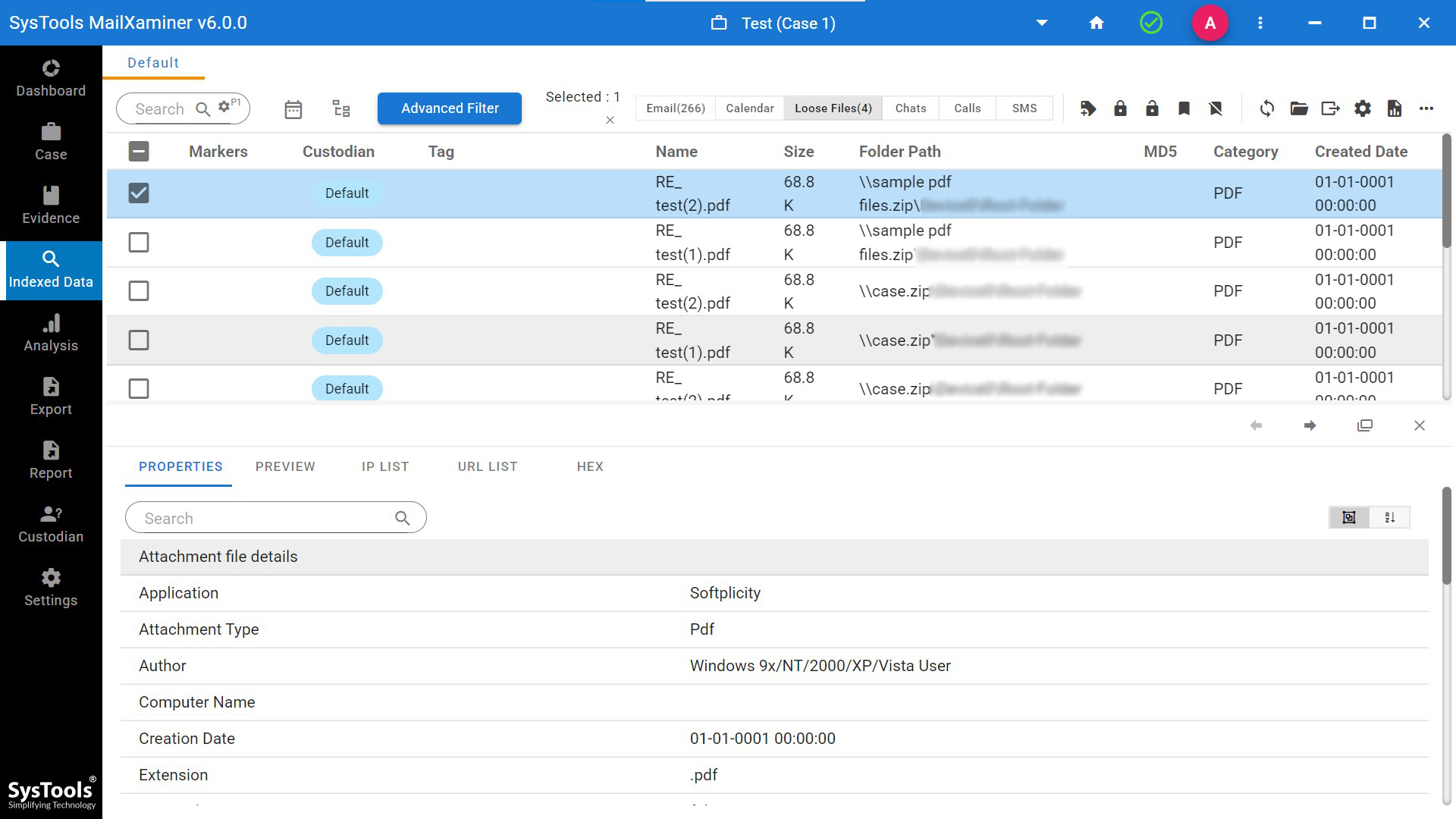
Step 4. Then you can see the properties, preview, IP List, URL List, and HEX of the files.
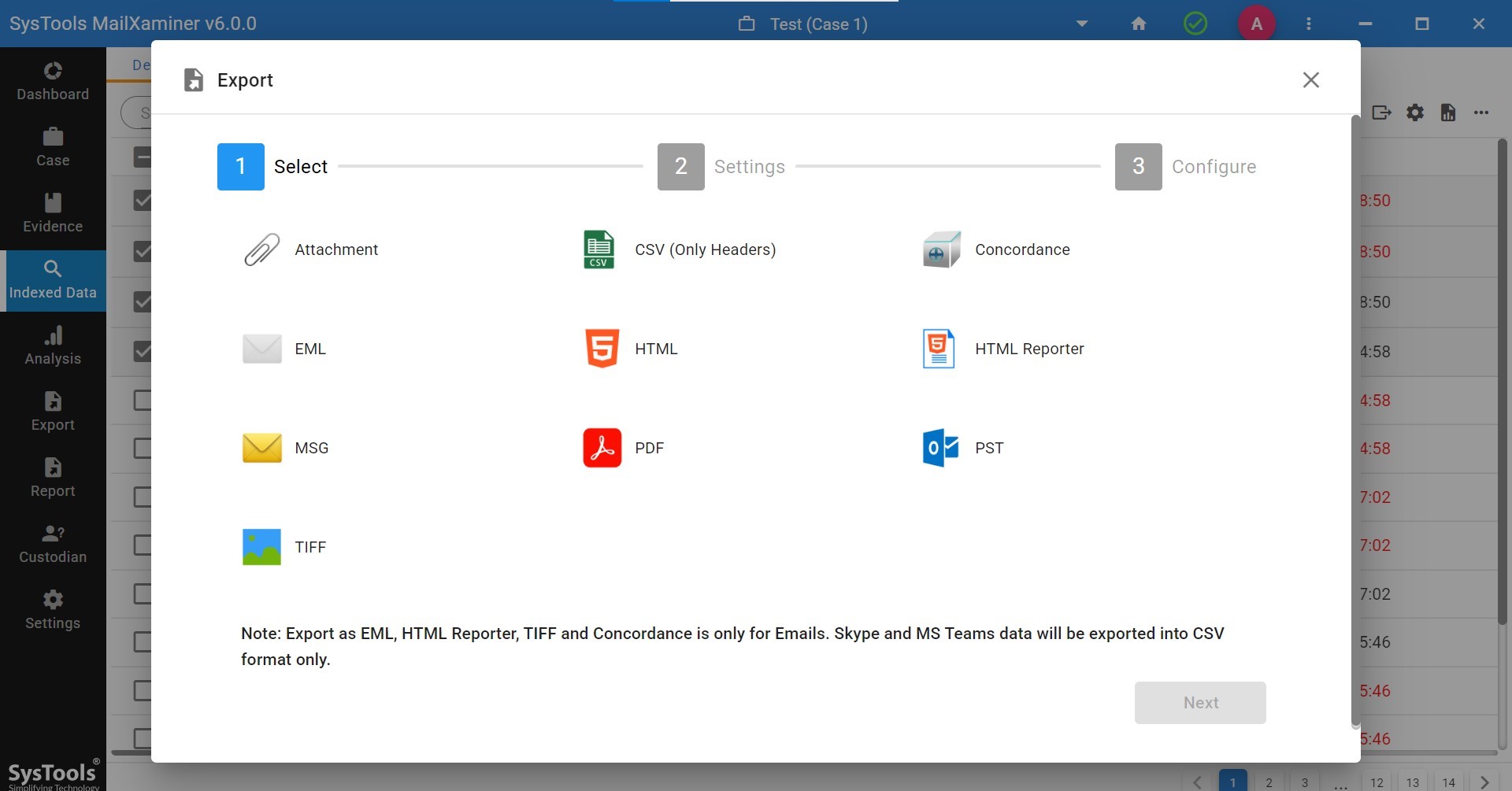
Step 5. Lastly, export the selected files into the preferred file formats.
Conlusion
Loose file analysis plays a very crucial role in uncovering hidden evidence that traditional methods often miss. These files offer crucial insights in digital investigations from deleted documents to fragmented data. It’s important to perform loose file forensics through authorized and highly expert-recommended software and techniques. In today’s fast-moving cyber landscape, this skill isn’t just helpful—it’s essential.
Therefore, whether you’re a seasoned analyst or just starting, loose file forensics is a core competency you can’t afford to ignore.

