KMail Email Forensics – Linux Email Client Insights
KMail is a user-friendly email client introduced by KDE (K Desktop Environment) for Linux, Ubuntu, and other UNIX systems. It offers a featured GUI interface for sending and receiving email messages. Furthermore, it is efficient enough to support several email protocols such as POP3, IMAP, Microsoft Exchange Server, and more. KMail is administered under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL), Version 2.
Moreover, it is a part of the private data manager that we call Kontact. Kontact is a personal data manager and groupware software package suite developed by KDE. It supports emails, to-do lists, news, calendars, contacts, etc. It offers various UIs apart from KMail such as KAddressBook, Akregator, KNotes, etc. KMail contains secure settings to take care of the user’s privacy with great end-to-end encryption and spam detection.
KMail Can Save Email Messages in Two Formats
Using KMail, it is possible to save messages in the following file formats:
- MBOX
An MBOX is an associate email mailbox that users take in use for storing and organizing emails. The MBOX file contains Inbox, Outbox, Sent Mail, Trash, Drafts, and Templates. These folders have special functions of storing, holding, editing, etc. emails. MBOX file was originally hosted by UNIX operating system but later, it collectively supported by many other email applications like Apple Mail, Mozilla Thunderbird, etc. - MailDir
It is an associate email format that can be used to store messages solely. It provides a various organized and systematic manner of storing mailbox information. It was initially introduced by a Qmail client and later employed by several alternative applications like Mozilla Thunderbird. It creates a separate file with a distinct name for every incoming message.
KMail uses the MailDir format by default. If you would like to alter your email application and wish to access your previous emails, in this probability you will not be able to open the emails. However, processing emails in MBOX format is not a problem.
KMail: Its Concept and Storage Type
KMail is the default email client of the KDE desktop environment. However, you will be able to additionally install it separately from the Ubuntu software package center run on GNOME surroundings. KMail supports Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), Post Office Protocol (POP3), and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). Using these protocols, a user can create multiple accounts as per the requirement. KMail is an anti-spam system and it supports hypertext markup language emails, OpenPGP, MIME, S/MIME email formats.
Before using KMail, you need to configure it for composing and receiving the emails.
For the KMail email forensics investigation, one has to configure the user’s email account in KMail email client. This configuration can be done from the ‘Settings’ of the KMail email client. The configured client window contains options such as Identities, Accounts, Appearance, Composer, Security, and Misc Folders.
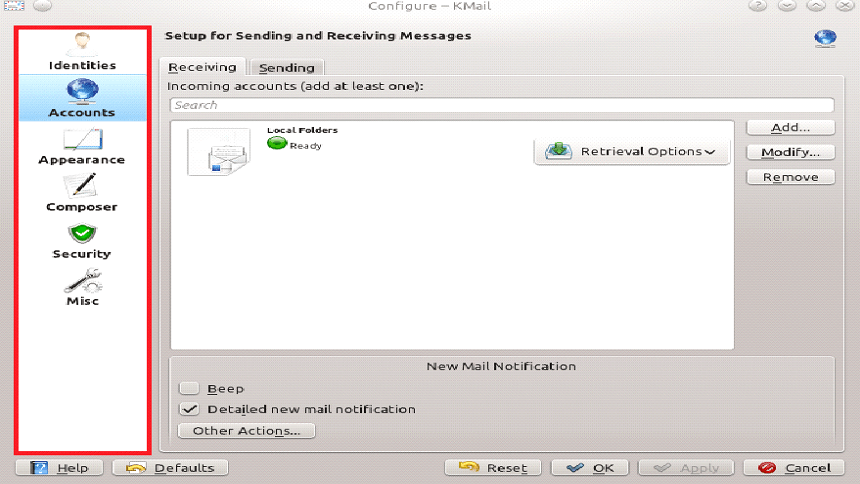
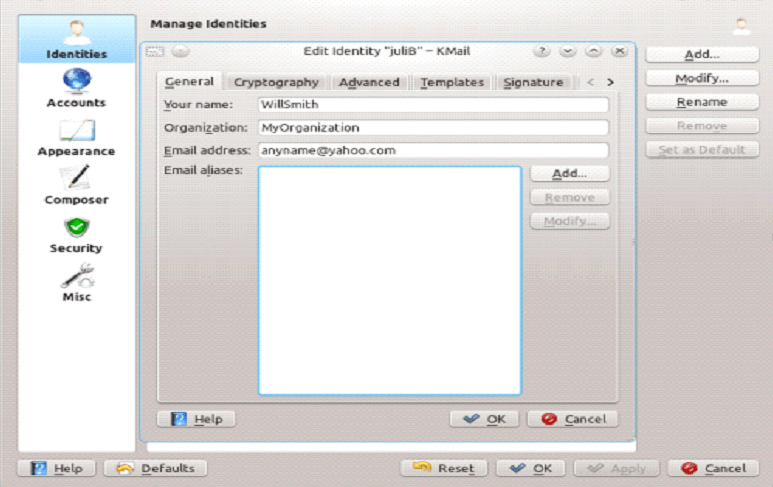
To begin sending and receiving messages, you need to modify the setting of Identities and Network tabs. Users must have to take all the email data from the service provider or administrator, to fill within the required data. Once you have done with filling all the required details correctly, you will be able to use your email account.
Key Features of KMail Email Client
- KMail supports normal email protocols like IMAP, POP3, and SMTP.
- It additionally supports authentication via NTLM (Microsoft Windows) and GSSAPI (Kerberos).
- Supports plain text and secure logins, exploitation SSL, and TLS.
- Integration of international character sets.
- Spell-checking (as-you-type and on-demand).
- KMail also provides native support for inline OpenPGP, PGP/MIME, and S/MIME encryption.
- Reading and writing of all the markup languages mail such as HTML, XML, etc.
- Ability to show plain text solely from associate markup language mail.
- Integration within style spam checkers, e.g. Spam Assassin, Bogo filter, etc.
- An optional spam chance meter can be displayed.
- Offers advanced search option and filter skills where a user can create its own search filter.
- Import option for several alternative clients/formats.
- Highly integrated with Kontact components.
- Facility to save encrypted password in credentials management application called KWallet.
- Several backup options such as manual archiving, automatic archiving, and exporting.
KMail Email Forensics Investigation
From an investigative standpoint, email has emerged as the widely used communication medium over the internet. It consists of communication through messages, delivery of documents, carrying out various transactions, etc. However, cybercriminals continue to misuse it for illegitimate purposes. As mentioned above, KMail will save all its messages in either MBOX or Maildir format.
Whenever a technocrat receives spam or malicious KMail message file associated with MBOX format, forensic experts start analyzing that MBOX file for forensic examination purposes. During the analysis process, investigators usually analyze all the data of suspect email without configuring it with the email client, by using an email forensic tool instead. So, to recover the shreds of proof from the messages of the KMail email client, it is recommended to use the efficient MailXaminer Email Examiner Software which is the best option.
This software can help the investigators to implement advanced level investigation to analyze the email data. It is capable to process 20+ email clients and 80+ email file types. This software offers numerous other features to analyze the email data in detail like Bulk Email Files Processing, Powerful Search Mechanism, Multiple Preview Modes, Reporting and Exporting, etc. In the next section, we will discuss these features in detail.
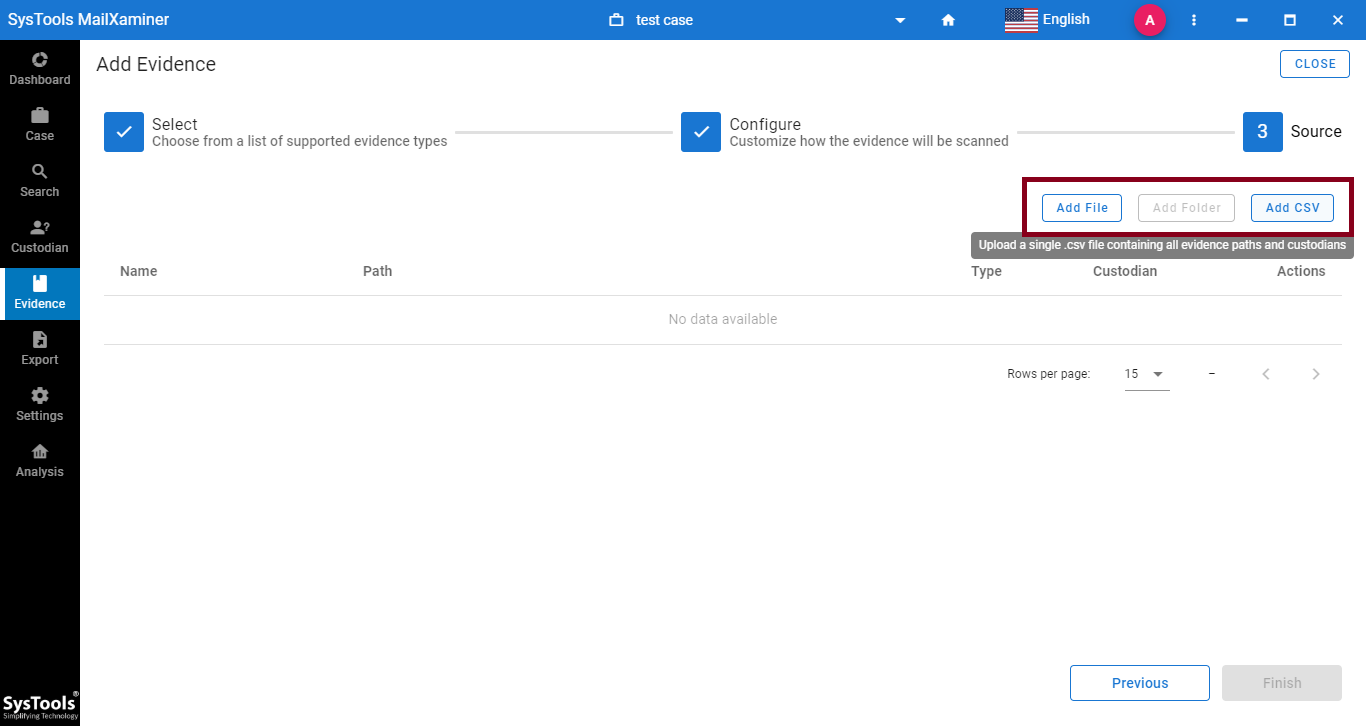
Bulk Email Files Processing
This automated tool provides support to process a large volume of email files for investigation. Users can process single as well as bulk email files by providing the CSV with the paths of multiple files or folders. It enables to process of multiple data files at the same time and users can also filter out the required data for examination by using its inbuilt filters and search options.
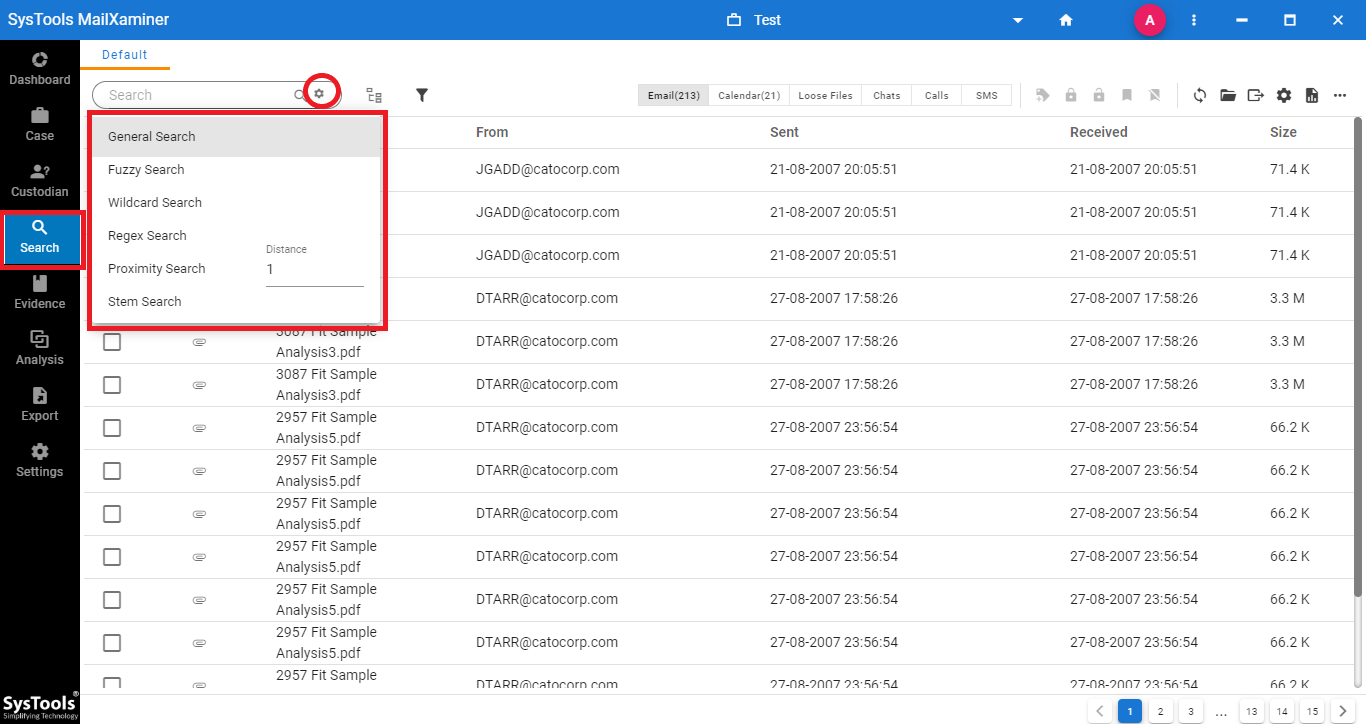
Powerful Search Mechanism
The tool has various searching options based on advanced algorithms such as General Search, Proximity Search, Regular Expression, Stem Search, Fuzzy Search, and Wildcard Search. These searching algorithms allow users to filter out the suspected data by entering related keywords. Users can easily search and analyze the suspected data to extract out the evidence. It’s crucial to know these factors in KMail email forensics.
Multiple Preview Modes
It provides multiple preview modes such as Normal Mail, Hex, Properties, Message Header, MIME, HTML, and RTF. It helps investigators to find and examine the email data in detail.
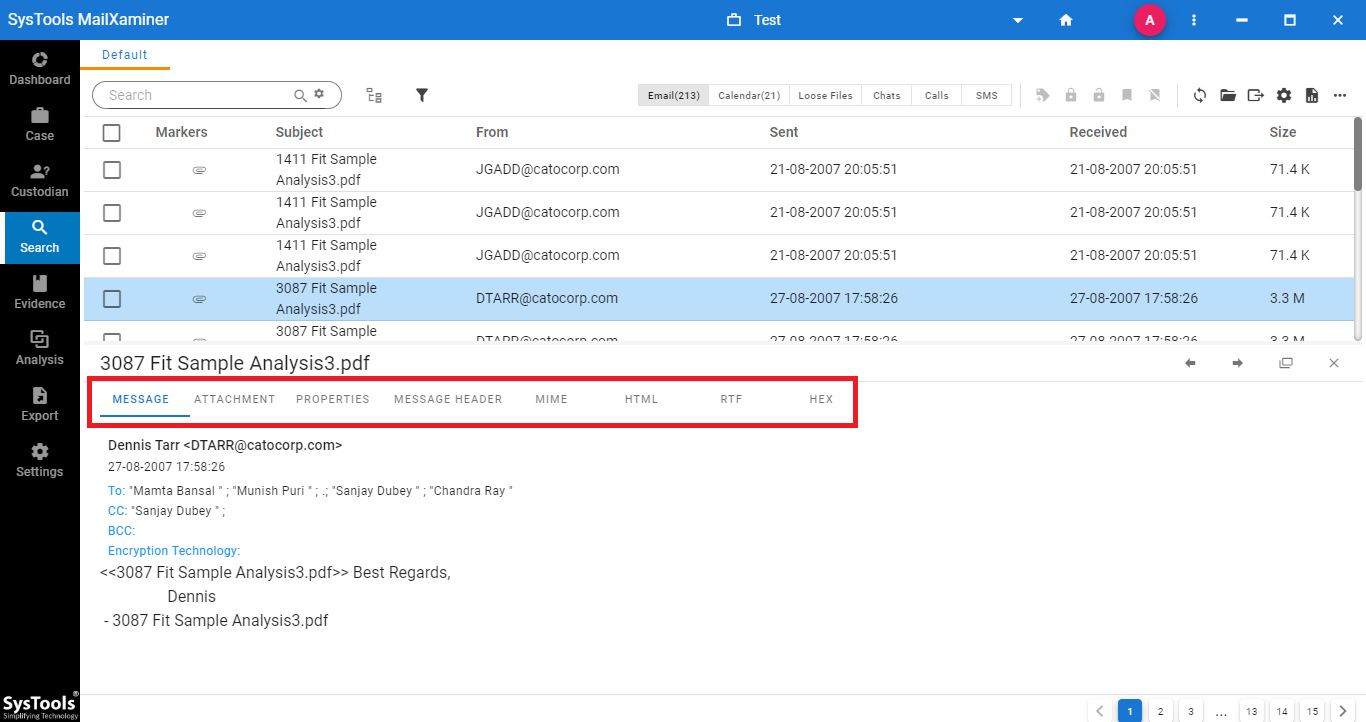
Reporting and Exporting Evidence Files
After analyzing and extracting the evidence from the suspect file, investigators need to report the evidence file. For this, the tool provides an option to Export the evidence that helps investigators to export evidential files in the desired file format and save at any destination location.
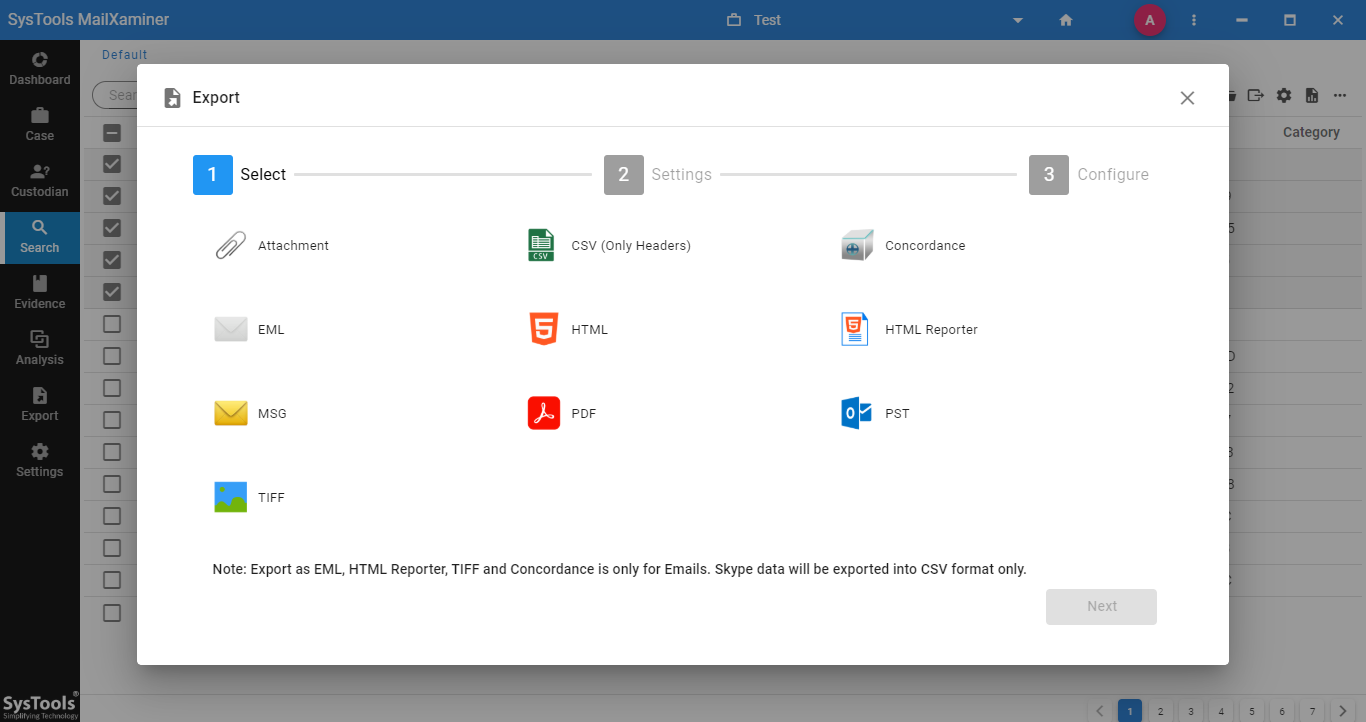
Summing Up
There, comes an instance wherein the investigators have to carry out KMail email forensics to investigate emails. For this, the above featured email forensic software is the finest utility to examine the data file generated by the KMail application. This email examination software has a wide range of advanced features and functionality that provides a hassle-free investigation to carve the hidden evidence.

