Memory Forensics- The Key to Recover Malicious Evidences
Memory forensics is a very significant digital forensic investigation technique that evidence examiners use to analyze the volatile memory (RAM) to discover cyber threats, malware, and system intrusions. Unlike traditional disk forensics, which examines static files stored on a hard drive, memory forensics provides real-time insights into a system’s active processes, network connections, and running applications.
When a computer is powered off, volatile memory is erased, making it a valuable but fleeting source of information. This is why live memory analysis plays a crucial role in incident response and forensic investigations. It allows examiners to detect malware in email, identify unauthorized access, and retrieve encryption keys or passwords that might otherwise be lost.
In this guide, we will explore the live volatile memory analysis through advanced techniques and solutions. Let’s discuss the comprehensive roadmap for memory forensics and cybersecurity.
What is Memory Forensics Investigation?

Live memory forensics process is done through capturing the current state of the system’s memory. Through the forensic analysis of volatile memory, the investigating officers can gather various information related to the data and the activities that have taken place in it. This includes the process that is currently running on the system, running executable files, IP address and other network information.
A memory dump is a snapshot of the system’s volatile memory at a specific point in time. Live memory forensics analysis provides valuable information about the state of the computer system before any malicious activity or crash occurs.
The RAM data stored in the dump can help to identify the reason for the incident and other related information. Through volatile memory forensics, the investigators collect the system’s volatile information and create a permanent record of the system’s state. Moreover, it helps to track different suspicious activities such as viruses and other malware attacks.
Why is Memory Forensics Important?
With every passing year, the attacking methods are getting more sophisticated. As a result, the importance of live memory forensics and the need for advanced solutions also increases.
Different network-based security solutions, such as antivirus software, firewalls, etc., fail to identify phishing email activities that have taken place in the computer’s physical memory. The forensic analysis of computer memory provides a unique insight into the current activities and network connections.
In many situations, the important data that leads to unauthorized activity or attack will merely exist in the computer’s volatile memory. The information, such as credentials, chat messages, running processes, internet history, which cannot be cached, etc. will be loaded in the physical memory. These make the memory forensics more complicated during the evidence collection.
Types of Memory Dumps Used in Forensic Analysis
Now you might be thinking why forensic analysis of volatile memory or RAM is not a part of every computer forensic investigation.
- Raw Formatted: It is the format used when the evidential data is being extracted from the live environment.
- Crash Dump: Before the system crashes or the occurrence of any error, the system automatically creates a memory dump file. It consists of a copy of computer memory, which helps the investigating officers to easily identify the problem that has led to a system crash.
- VMWare Snapshot: It contains a snapshot of the virtual machine. Moreover, it provides the exact state of the machine at the time the snapshot was generated.
- Hibernation File: This file consists of the system’s snapshot that the operating system can return to after hibernation.
- Page File: This file will contain the information, which is similar to the data stored in the RAM.
Best Automated Method to Perform Live Memory Forensics
One possible approach to overcome all the possible challenges in memory forensics is to implement continuous live monitoring, conduct multiple scans, and actively detect malicious patterns.
However, with modern computers typically having at least 8GB of RAM—and many exceeding 32GB—analyzing a full RAM dump becomes an increasingly labor-intensive process.
Moreover, scanning such vast amounts of data in real time to catch malware before it causes harm is often impractical. MailXaminer is the software that can become a need of the hour. This email investigation software is especially designed for handling digital forensic investigations huge tasks.
- Network Connections: It contains the option of link analysis information, such as IP address and port number used in the past and current network connections. This will help to identify the remote destination of malware communication, computer intrusion, etc. During the memory dump forensic analysis, the investigation officer can identify the type of traffic that was used in the communication vector, like HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc.
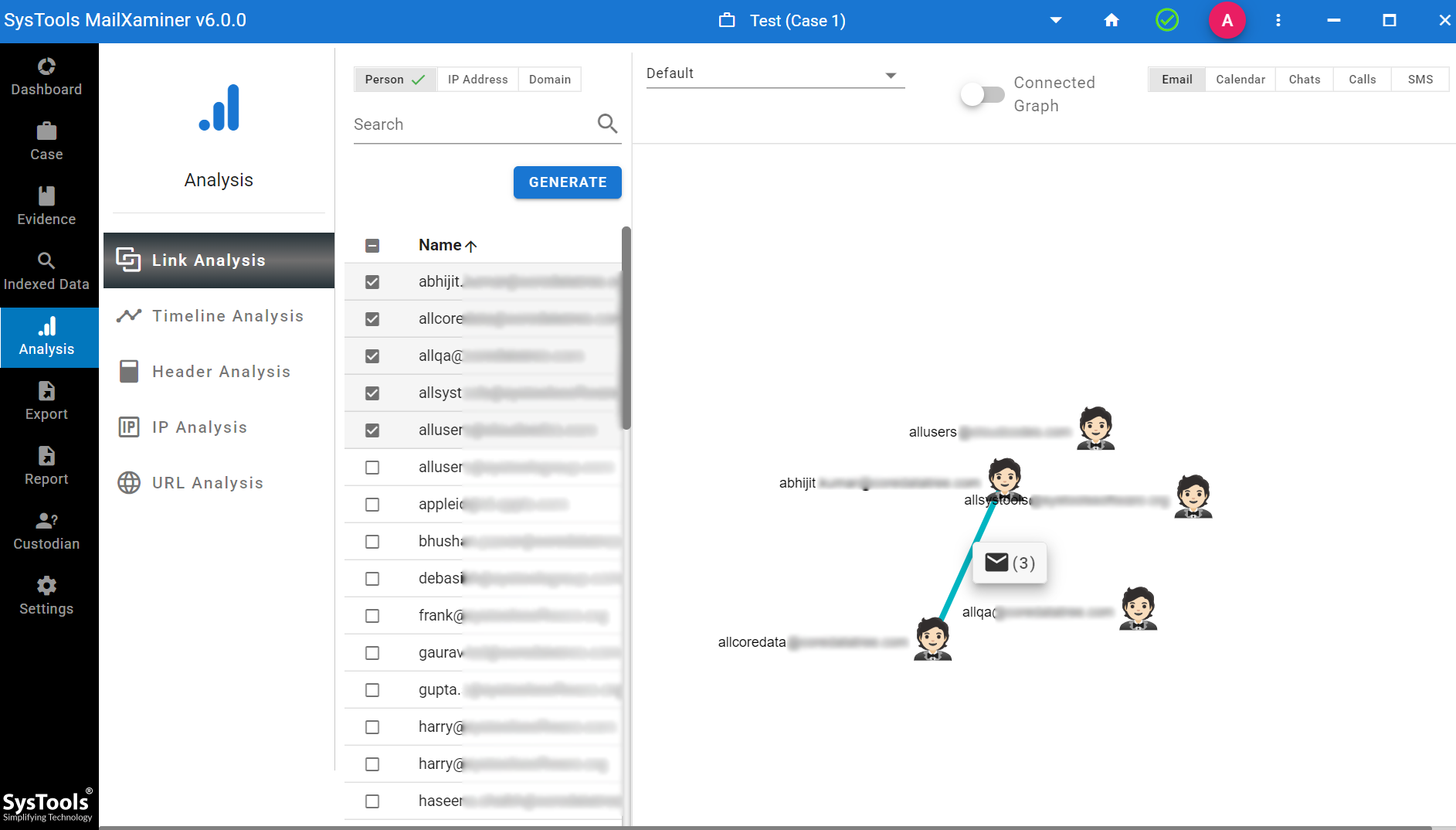
- Decrypted Version of Programs: If any evidence file is added with the encryption, it simply decrypts the file and adds the evidence.
- Malware Resides in the Memory: The malware, which resides in the system memory, will not leave any digital footprint in the hard drive. Therefore, any data collected by the malware is also stored in the system’s memory, and this software detects the malware containing emails in the dashboard.
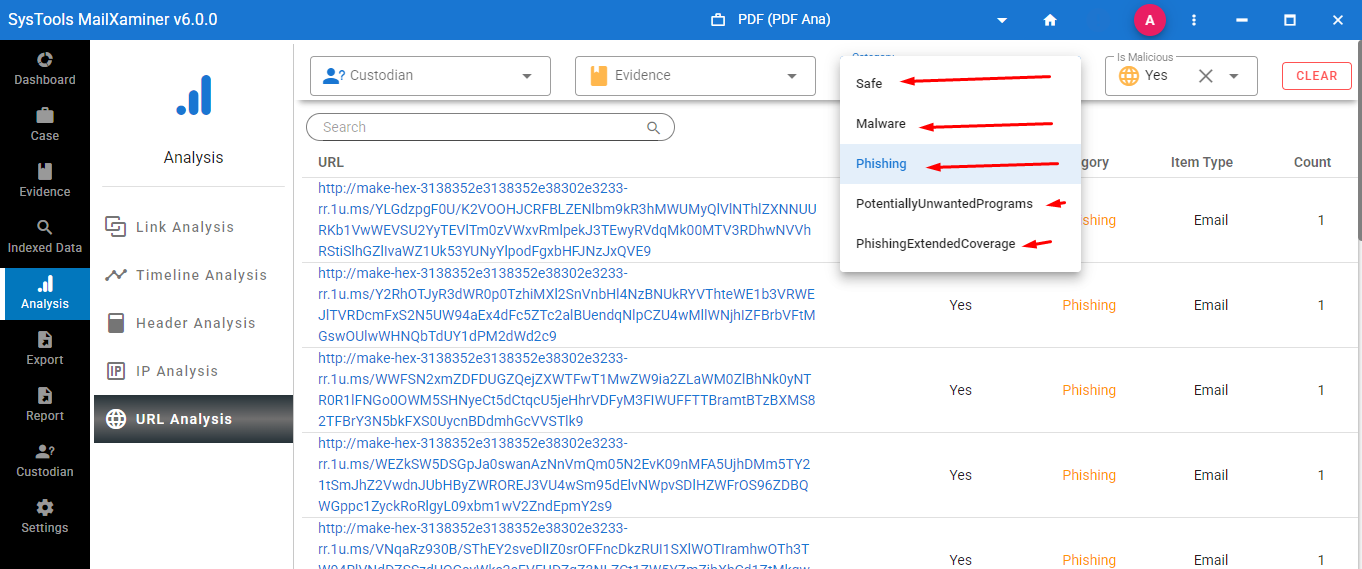
Key Features of the Software for Smart Memory Forensics
In the fast-changing domain of RAM, cybersecurity specialists and investigators need to prioritize detection, as well as the neutralization, of threats in real time.
This advanced software provides a protective barrier against attackers by continuously randomizing memory use within an application, therefore making it much more difficult for sophisticated threats to leverage vulnerabilities in computer memory.
In combination with real-time monitoring of applications installed, the cybersecurity team can carry out rapid incident response. In addition, forensic investigators can begin the data acquisition process, quickly capturing vital evidence early on, before it disappears.
Investigation of these threats is very important, in cloud forensic investigation of threats that are based on email. Email is still the primary attack vector for phishing, malware delivery, and command-and-control communication, and this tool allows forensic experts to extract, analyze, and correlate email artifacts with the data captured from volatile memory.
The combination of this solution and live memory analysis applications provides a collection of tools that maximizes the investigator’s capabilities for incident response and prevents any gaps from being left.
Closing Remarks
Memory forensics is the process of acquiring evidence from computer memory. It helps the investigating officers to identify the crucial data and malware activities. With the expertise in live volatile memory analysis, forensic experts can discover the hidden threats and prevent critical systems from cyberattacks. This blog has clearly stated the forensic analysis of volatile memory, which provides detailed information about the running system and its processes.

