Pocomail Email Forensic Analysis – View Pocomail MBX File
Even though email service providers like Pocomail email client have resolved the issues pertaining to spam and Denial of Service attacks. There are still several existing litigation cases involving spam messages and network intrusions. While having contravention in email security among the organizations, a thorough investigation is crucial to determine the reason for the unlawful act. Pocomail email forensic here helps in getting all the evidence related to a particular crime or project.
Let us first acquire a brief understanding of Pocomail email client, and then proceed to its forensic implication. It can help the investigator to resolve different forgery techniques applied by the hacker to tamper an email message.
Exploring Pocomail Email Client
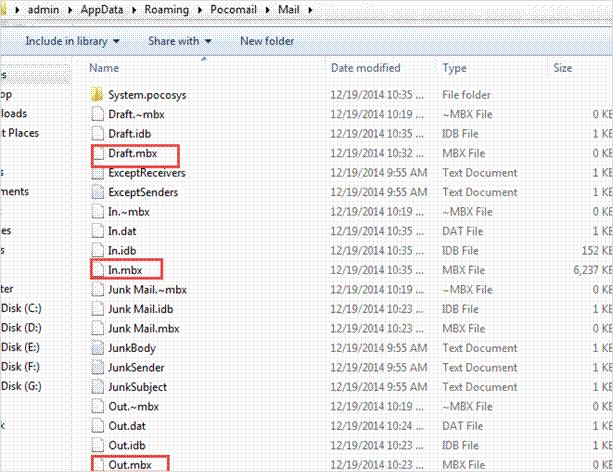
Pocomail is one of the popular email client with a design compatible with Microsoft Windows OS. It has its inbuilt scripting features that we call “PocoScript”. Moreover, it can be a connector between Pocomail and external applications such as PGP encryption and FTP processing. It helps in securing the network and protecting the email messages from hackers. On installing the Pocomail client and successfully synchronizing it with the Gmail account, one can notice all the data gets saved in the “Mail” folder, which is present in the folder update.
The default path location for locating the messages is there below:
C:/Users/admin/AppData/Roaming/Pocomail/Mail
All the messages in the Pocomail is there in an MBX file format.
Also Read: Best Guide on Email Forensics In Outlook Mac OLM File
Manipulation of Data on Pocomail Email Client
Pocomail email client installed on the user’s machine needs to be synchronized with Gmail account working on the Gmail server. There is a possibility to spoof the IP address of the email data by the remote attacker. An attacker can access the Gmail server by synchronizing through Pocomail email client and can forge the data easily.
An attacker can take spam messages to instigate an attack on the Pocomail email account. By delivering bulk spam messages to one’s Pocomail account, they can exhaust the user’s quota of sending or receiving email messages. Thus, it indirectly affects the Gmail account located on the server. Generally, such attacks constitute a type of cyber-attack which is known as Denial–of–Service attacks.
How Denial–Of–Service Attack Takes Place?
In the case of Denial-of-Service attack, the hacker makes an attempt to resist or stop user’s approach to their own data. It usually targets the user’s system and its network connection, or the websites which a Pocomail user is trying to browse. By doing so, they prevent users from accessing web pages, online accounts, or email messages.
The most predictable pattern of the DoS attack happens when a hacker floods a network with data. In such a case, when a user enters an URL to view a specific website from the browser, it will send a response to that particular site’s system server. The server can process only a limited number of requests at one time. Therefore, when the hacker strains the server with repeated requests at a time, the server is not able to process requests. Then, it makes the user unable to access the site.
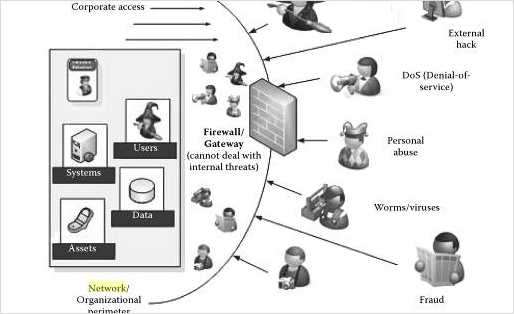
Pocomail Email Forensic Implications Related To Network Intrusions
Whenever cases related to network intrusions are identified in Pocomail, the very first step is to identify the type of attack initiated by a hacker to forge email. After finding out the pattern of attack, forensic investigators can adopt appropriate methods to obtain the domain name which helps them to identify the attacker.
During the forensic investigation of email crime, the major concern of investigators is to find out hidden clues and facts that can help to solve the hurdles of the case. For this, they try to adopt a method that ensures in-depth examination with no loss of data. To do so, they forensically analyze the Pocomail email information from the system. However, the process is not as simple as it seems to be.
Types of Attacks
The hackers use different techniques to conduct attacks using IP addresses. Some of these are here below:
Spoofed IP Address:
Some hackers make use of deceptive IP addresses. Generally, spoofing becomes difficult to execute attacks that need connections to be set up. Therefore, attackers use it when there is no requirement to establish a connection.
IP Addresses Targeted from Many Sources:
Sometimes it is noticible that the attacker uses a different source of IP addresses. Such as in the case of DoS attacks, this depends on several machines that have been taken over for executing an integrated attack.
The legitimacy of an IP Address:
Often IP address allocation is vigorous. In such a case, the machine which is operating with a specific IP address may not be the same system that was there when the attack happened.
IP Traceback:
The IP traceback approach includes the method to recognize the origin of attack packets. Some of the tracing approaches involve inquiring about network routers of traffic. They develop an effective overlay network by employing a logging mechanism to track the selective flow of data packets. It clears the attack path by reformation, employing an IP packet with initiation by routers in course of attack.
Re-tracing of Attacks and Reformation
These days internet attacks related to worms and viruses have become an inevitable threat among organizations. The viruses or worms don’t require any user connection to proliferate as they are self-propagating and self-sustaining blocks of generated code. Tracking the origin of such kinds of worms has become an important part of forensic activity.
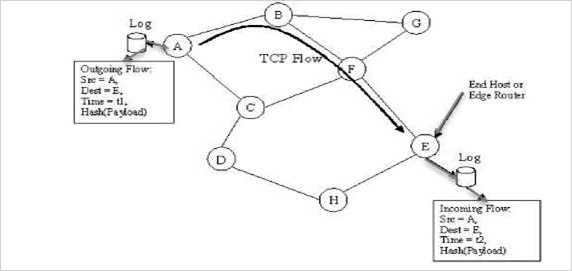
Here, the figure below shows a simple illustration of path traced between two nodes in a network. Node A is the source and node E is the destination. If we identify node E as the malignant stream of code, then node E looks for its table for the incoming flow of data to identify the source of the vicious flow of data. Then, node E can employ a request protocol to figure out the source of the malignant bitstream. The details of data flow can be appropriately stored in network routers rather than the user’s system to eliminate the possibility of any data alteration to end-users.
Conclusion
The different approaches above explicitly shows how to handle tampered messages in Pocomail forensically. But often, investigators need a solution that can help them to easily locate, view, and analyze Pocomail messages with the least efforts. One such third-party tool that offers such kind of convenience to examine the emails forensically is MailXaminer. This is the best way to conduct Pocomail Email Forensic investigations. It supports 80+ email clients and more than 20 email formats to view messages efficiently.

